T Hillmann1 , S Sutharsan2, R Costa3, J Suggett3
1 Department of Pulmonary Medicine, University Hospital Essen - Ruhrlandklinik, University of Duisburg-Essen, Essen, Germany
2 Department of Pulmonary Medicine, University Hospital Essen - Ruhrlandklinik, Adult Cystic Fibrosis Center, University of Duisburg-Essen, Essen, Germany
3 Trudell Medical International, London, Ontario, Canada
INTRODUCTION
OPEP devices are crucial for airway clearance in patients with excessive mucus production, including those with bronchiectasis, cystic fibrosis
(CF) and COPD. This laboratory study compared the performance of four different OPEP devices, each utilizing distinctly different mechanisms to generate oscillatory pressure. Flow oscillation amplitude (the magnitude of pulse), was determined at an average positive pressure of 15 cm H2O, a midpoint within the therapeutic range of 10 – 20 cm H2O typically targeted for OPEP devices.1 Higher oscillation amplitudes may create stronger shear forces, reducing the viscoelastic properties of bronchial secretions1 and enhancing mobilization and clearance.2
METHODS
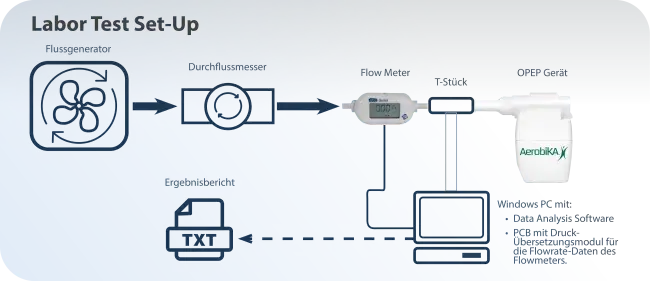
Four OPEP devices were assessed at their mid resistance setting(s) using a flow generator (Resmed VPAP III), flow meter (TSI 4000) and pressure sensor for data collection and analysis. The OPEP devices that were evaluated included the Aerobika* (Trudell Medical International), Acapella Choice* Blue (ICU Medical), GeloMuc* (Pohl Boskamp), and RC – Cornet* Plus (Cegla) devices. For each OPEP device, 3 devices were tested (n=3) with tests repeated 3 times. The average flow oscillation amplitude was measured for each device when the positive pressure was set at 15 cm H2O.

RESULTS/DISCUSSION
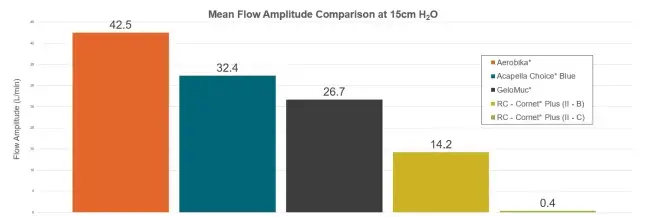
The four OPEP devices exhibited varying performance, with the Aerobika* device achieving the highest flow pulse amplitude, followed by Acapella Choice* Blue, GeloMuc*, and RC - Cornet* Plus. Notably, the RC – Cornet* Plus demonstrated inconsistent oscillations at its higher mid-resistance setting (II - C) due to inadequate flow rates, with more reliable results at the lower mid-resistance setting (II – B).
DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION
The Aerobika* OPEP device demonstrated the highest average flow pulse amplitudes at the target pressure setting. Higher oscillation amplitudes may create stronger shear forces, reducing the viscoelastic properties of bronchial secretions and enhancing mobilization and clearance1,2. Limitations of the study include recognition that the clinical impact of such differences in flow amplitudes should be proven in patients and that patients may not always operate their OPEP devices at the target 15 cm H2O positive pressure.2 When selecting an OPEP device, it is crucial to consider not only the clinical evidence supporting its efficacy and patient preferences but also the variations in mechanical mode of operation that can influence device performance.
